Things that affect video quality: Resolution, Color depth, Frame rate, Bitrate
Videos are becoming a very significant part of our everyday life. The report from The Social Shepherd in 2023 reveals that people watch videos for 84 minutes every day worldwide. Social platforms such as TikTok and YouTube are heavily invested in promoting multiple kinds of video content. As video has become the world's dominant form of entertainment, it’s nice to learn more about them. Consumers always want videos with high quality and a smooth experience when watching them. So let’s explore which factors affect or decide a video quality.
Video resolution
Video resolution determines the number of pixels contained in each frame. Resolution is calculated by the width and height of a frame. For example, when the resolution of a video is 4080 x 3072, that means that there are 4080 pixels in the width and 3072 pixels in the height of the video. Therefore, each frame of that video has approximately 12.5 million pixels in total. Generally, the more pixels you have, the sharper and better your video will be.

Nowadays, the standard for video resolution is at least HD (720p) or Full HD (1080p), anything below that is considered low-quality. Screen resolutions on computer monitors and televisions have improved, some of which can support up to 12K resolution. Though most of the time, you don’t need this extremely high-res option. The trade-off here is the more data you have, the more resource requires to store, transfer and process them.

Color depth
Every pixel in a digital image is a combination of the three primary colors: red, green, and blue, often referred to as a "color channel". Color depth, also known as a bit depth or pixel depth, refers to the number of bits per pixel to represent a specific color. A 24-bit JPEG image (8-bit per channel RGB) can display approximately 16 million colors.

As you can see, images with higher bit depth give you a higher quality and are more realistic. Scientists estimated the human eye can perceive up to 10 million colors. Anything beyond that is not distinguishable to the human eye, but will still appear more colorful when being processed by the brain. In digital photography, 24-bit color is a standard and tends to be called ”true color”. The higher the number of colors a pixel can display, the better the tone and clarity of the photo.
Frame rate
Video is a series of still images that, when viewed in order at a certain speed, give the appearance of motion. The number of frames per second (fps) in a video is what we call the frame rate. A frame rate of 24 fps denotes that 24 images are displayed in a single second.



Each frame rate has a specific use case. To decide what frame rate will work best in certain cases, there are some factors, such as:
How big is the acceptable file size? The higher the recording frame rate is, the larger the video file size will be
How fast the objects in your video are moving? To capture and display fast-moving objects, a higher frame rate like 60 FPS is more suitable.
Does the video need more editing or processing? The more frame a video has, the more resource needed to process that video.
24–30 fps became the standard frame rate for movies and television because it used the lowest amount of film while achieving natural motion to the human eye. While in the gaming industry, 60 fps is a magic number, especially for fast-paced games with a lot of action.
Bitrate
We have discussed video resolution, color depth, and frame rate. Now it’s time to put all the pieces together.
Resolution tells us the number of pixels in each frame.
Each pixel contains some data to represent a specific color.
Frame rate let us know how many frames are displayed in a single second.
So if we multiply those things together, we can find out the theoretical amount of data needed to record in a second. The amount of information per second in the video is known as bitrate. Bitrate is measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (Kbps), or megabits per second (Mbps). More bits mean more information, which means higher-quality video.
Deciding on bitrate is a tradeoff between quality and functionality. A higher bitrate increases the size of your file, which can make it slower to export and transfer. A lower bitrate will give you a smaller file size, but your video quality will not be as good. Once again, it’s all about finding the right balance.
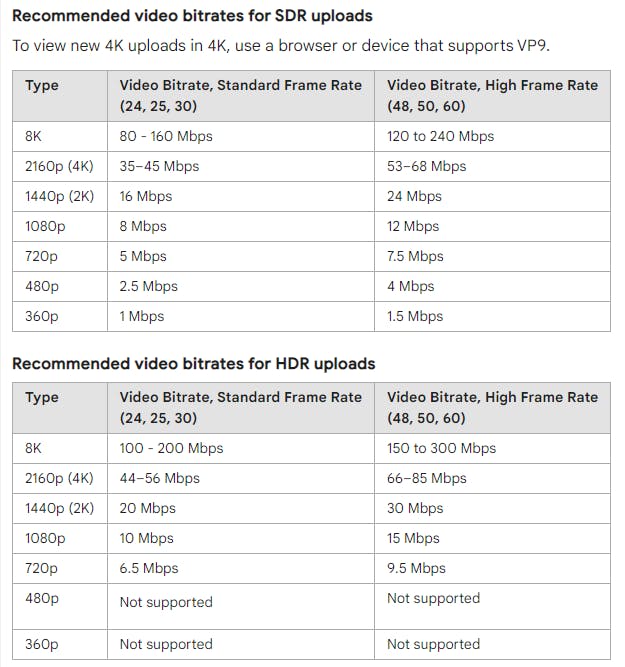
Below is the bitrate recommendation from YouTube for uploaded videos:
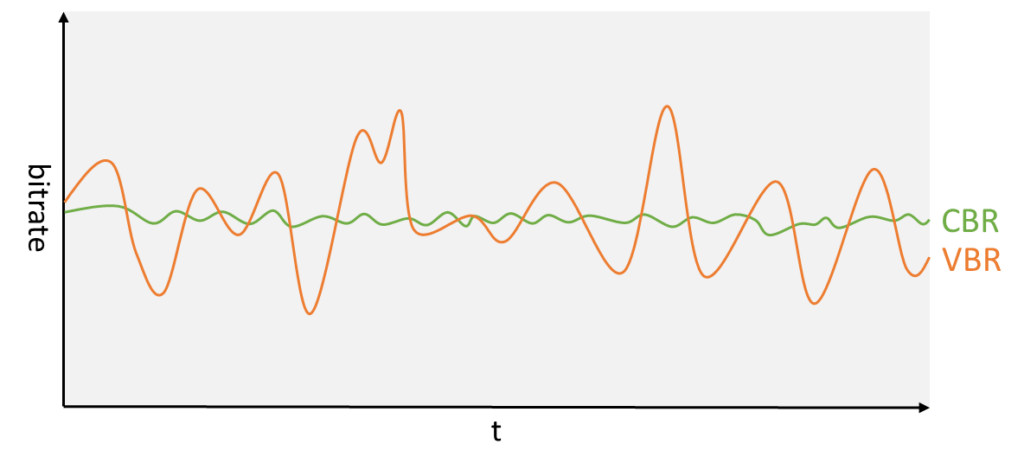
There are two different types of bitrate: variable and constant. Constant bit rate (CBR) maintains a consistent bit rate throughout the entire playback of the video. This makes videos easy to play and quick to load, since everything is constant from start to finish.
Variable bit rate (VBR) uses a dynamic bit rate that changes throughout playback, depending on the level of detail needed. Slow scenes use fewer bits than fast-moving, action-packed scenes. VBR is typically harder for devices to play back - since the bit rate constantly changes - but it provides much higher video quality without massive file sizes.
Now, it’s time to do some math. Let’s say we record a video with a resolution of 1920x1080, which mean a total of 2,073,600 pixels per frame. With a frame rate of 30fps, we have to display 62,208,000 pixels per second. Assuming each pixel contains 24 bits, we need about 1493 megabits (~186.625 MB) for just a single second in the video. With a 3 minutes video, that is approximately 33.6 GB in size, a ridiculously large number. But you have probably never seen a 3-minute video that big, so what is the catch? Fortunately, there are ways to compress that data and omitted redundancy information without affecting much of the quality.
How does it work? Let’s find out in the next part: video compression. Thanks for reading.
References
Video Frame Rate, Bitrate, & Resolution MADE SIMPLE
